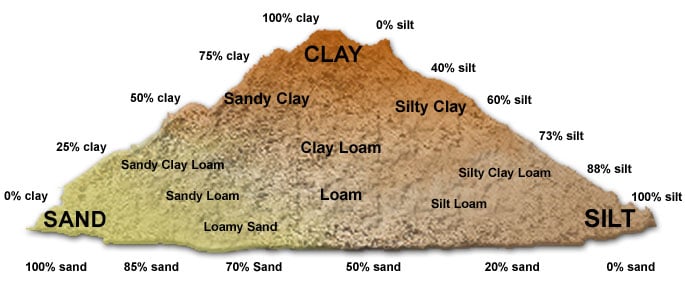
There are typically 6 main types of soils you will come across:
- Sandy,
- Loamy
- Clay and
- Silt
- Peaty
- Chalky
The first 4 can further break down by the % of one vs. the other. See diagram below:
Each has its pros and cons and can be great for various plants.
Clay soil:
Clay soil will clump together. It has poor drainage but is good for many evergreens like asters, shrubs, and even some vegetables.
Sandy Soil
Usually, Sandy Soil is the loose soil that does not hold together in your hand which means it is quick to dry out and takes its nutritional value with them. Tulips do well in sandy soils much like rooted vegetables like carrots and parsnips.
Silty Soil
Silty soil is soft, soapy, and can be easily compacted, making it ideal for grasses and moisture-loving trees like Willows, and shrubs. You can improve the drainage with the organic matter also.
Loamy Soil
Loamy Soil is often regarded as the best soil type for gardeners as it blends the defining characteristics of all the other soil types making it fine in texture, damp enough, and with good structure.
Peaty Soil
Peaty Soil is spongy and darker in colour. It’s good for growing vegetables and will keep shrubs like rhododendron and camellia happy too.
Chalky Soil
This is a fairly shallow and Stoney type of soil that is calcium-rich which makes it high in Ph (7.1 – 8). It’s good for trees, shrubs, and many bulbs. Vegetables such as spinach and cabbage will also do well.
Most of you will notice when you purchase plants, that they have a soil pH level that it prefers, try matching this to create the best soil for your needs.